masculinities
मोहनस्वामी – लेखक वसुधेंद्र अनुवाद – रश्मि तेरदल (हार्पर पेरेनियल Harper Perennial, 2016) जब मैं छात्र जीवन में पढे गए…
Traditional masculinity is not without its problems but to eliminate its component of stoicism is to pull the rug from under a cast of tough and determined characters who make society function.
There is someone in my life who had a terrible childhood, has had several liaisons and whose father married twice. He says that he hated his father. How would his father react to his son’s liaisons if he were alive? If I love a cyborg or a person of the same gender, how will my father react?
Is a moustache synonymous with the socially established understanding of what makes a ‘man’, is it what marks the degree of manliness, or rather, the degree of male privilege, and is it something that defines the kind of relationships men share with each other?
In a patriarchal society, masculinities manifest or show-up as a very particular set of behaviours such as being controlling and dominating, often in violent ways. In fact, the root of masculinities in a patriarchal society emphasises practicing this violence and control.
Through its vivid and raw depictions of socio-cultural life in rural Karnataka, the author, Vasudhendra, a key voice in contemporary Kannada literature, brings forth his identity in all its intersecting dimensions, through the inclusion of class, caste, religion, gender, rural-urban location, education and language.
This malignancy of toxic masculinity is a mutant inheritance that is hard to eradicate. However, initiating discussions about it and spreading awareness is essential to minimise the cost to its victims.
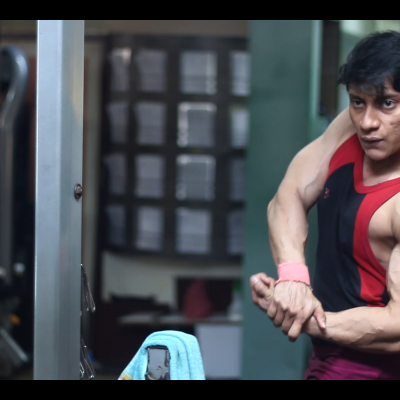
Social norms don’t expect women to look muscular, but if men are muscular, it is considered sexy. Just by choosing to pursue a largely male-dominated sport that glorifies what is accepted as “masculine”, Karuna and Sibalika are pushing the boundaries of these labels.
Whether it is by checking harassment from fellow men, or by questioning one’s own internalisation of subtly sexist and harmful behaviour, there’s a whole range of ways to go about making a positive shift
This immense pressure to perform masculinity throughout each day and night not only impacts men’s wellbeing, but it also inevitably impacts the way they interact with the world around them. These interactions – this performance of control over oneself and others – reinforce the social norms and norms of power that drive gender inequality.
The use of terms that convert the movement for women’s empowerment into extreme militancy in order to reject the movement altogether is indeed a sombre example of diverting attention from the real problems that exist in society and projecting women’s protests against sexual crimes or standing up for their rights as one of “mob lynchings” or wrongly adducing the news of repealing “Adultery” as a move that allows women to have sexual relations outside of marriage.
The social contract of family becomes the sexual contract of the state, i.e. by placing women within the ‘domestic space’ under the ‘control’ of the ‘right’ kind of men. During partition this played out in the ‘reclaiming’ of the ‘abducted women’.
Masculinity once upon a time was just a word we studied in school, whose sole purpose was to differentiate binary gender in the society. Now masculinity is a criteria of a certain job that a person has to perceive to be called or termed as one.
As these correlations between gender development, physical violence and mass shootings come into sharper relief, the term “toxic masculinity” has become a staple of public discourse used to characterise men like Connor Betts, and even Sandeep Singh.
प्रतिमा का यह एक-चला रूप, जिसकी उपासना पहचान और पहचान की राजनीति से जुड़े क्विअर समुदाय के लोग करते हैं, जैविक सम्बन्धों और विषमलैंगिकता के विचार पर बनी परिवार की इस परिभाषा को चुनौती देता है।